Wikipedia traffic trends: Why visits rise, fall, and what it means for open knowledge
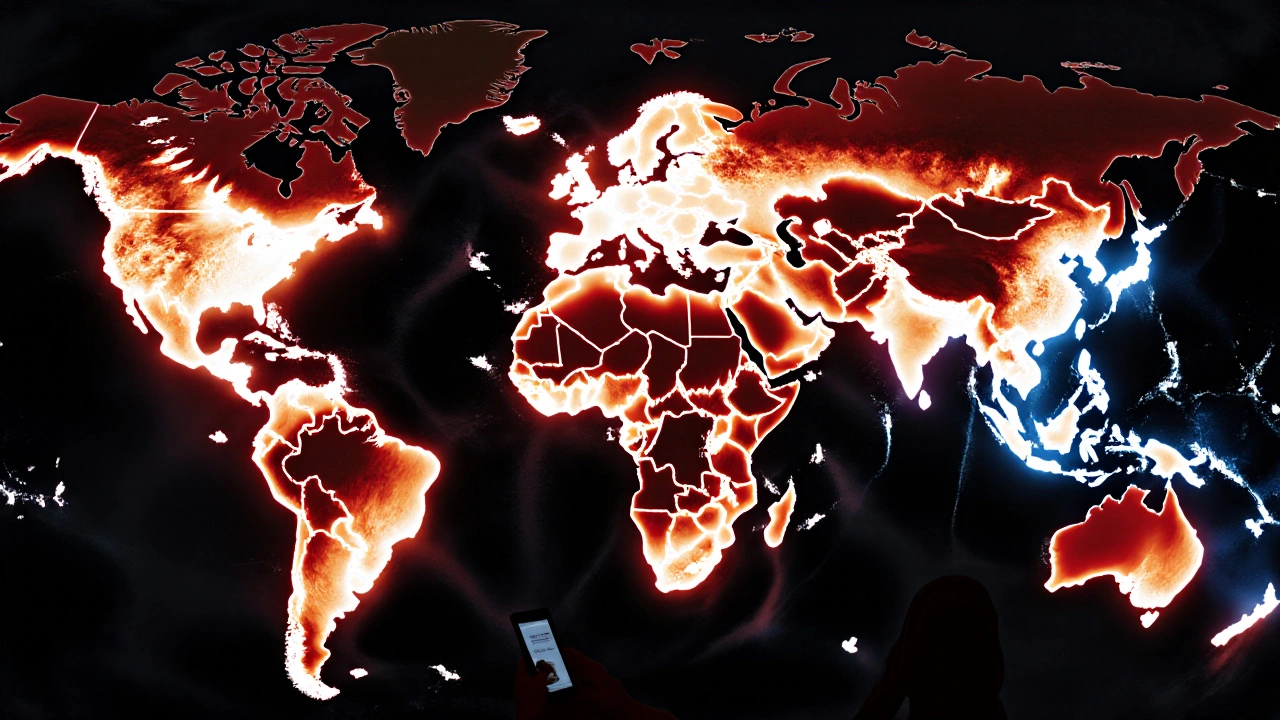
When you search for something online, chances are you land on Wikipedia traffic trends, the patterns of how many people visit Wikipedia over time, influenced by real-world events, search engine changes, and public trust in information. Also known as Wikipedia usage patterns, it’s not just about numbers—it’s about who’s looking, why, and what that says about the world’s reliance on open knowledge. Every day, over half a billion people visit Wikipedia. That’s more than any other encyclopedia in history. But those numbers don’t stay flat. They spike during elections, natural disasters, celebrity deaths, or when AI tools fail to give clear answers. When people realize AI summaries are wrong or missing context, they go back to Wikipedia—not because it’s perfect, but because it shows its sources.
What drives these spikes? It’s rarely advertising. It’s Wikipedia traffic, the real-time flow of users seeking verified facts during moments of uncertainty. Also known as Wikipedia search volume, it’s tied to global events. During the 2020 U.S. election, traffic to pages about voting systems jumped 400%. When the Ukraine war started, visits to related country pages hit record highs. Meanwhile, Wikimedia Foundation, the nonprofit that runs Wikipedia and keeps it running without ads. Also known as WMF, it doesn’t track clicks for profit—but it does monitor traffic to understand where misinformation is spreading and where help is needed. When AI companies scrape Wikipedia to train their models, traffic often dips slightly in certain regions because users think the answer is already inside the AI. But when those AI answers get caught lying, traffic surges again. People come back because Wikipedia doesn’t pretend to know everything—it shows you how to find out.
There’s also a quiet, steady decline in some areas. Younger users, raised on TikTok and AI chatbots, sometimes skip Wikipedia entirely. But when they need to cite a fact in a paper, verify a rumor, or understand a medical condition, they return. The real story behind Wikipedia traffic trends isn’t about competition with AI—it’s about trust. People still choose Wikipedia over flashy AI summaries because it’s transparent. You can see who wrote it, what sources they used, and how it changed over time. That’s something no algorithm can fake.
What follows is a collection of stories that explain how Wikipedia stays relevant, how editors respond to traffic spikes, and why the numbers don’t tell the whole story. You’ll find how volunteers track surges, how the foundation reacts to global events, and how even small changes in policy can ripple across millions of visits. These aren’t guesses—they’re real observations from people who watch the numbers every day.
Most Viewed Wikipedia Articles of the Week: What’s Trending and Why
Discover which Wikipedia articles drew the most views last week and why certain topics spike in traffic. Learn how news, culture, and volunteer editors shape what the world is searching for.
Fantasy and Sci-Fi Franchises on Wikipedia: How Fandom Drives Page Views
Fantasy and sci-fi franchises dominate Wikipedia traffic because passionate fan communities constantly update pages with new lore, character details, and episode summaries after every movie or show release.