Wikipedia editing: How volunteers shape the world's largest encyclopedia
When you think of Wikipedia editing, the collaborative process where volunteers write, fix, and update encyclopedia entries in real time. Also known as crowdsourced knowledge building, it’s what keeps Wikipedia alive without paid staff or ads. It’s not just typing words into a box—it’s a quiet, constant battle over truth, fairness, and what gets remembered. Every edit, every rollback, every discussion on a talk page is part of a system designed to let anyone help, but only if they follow the rules.
Behind every clean article is a network of Wikipedia volunteers, tens of thousands of unpaid people who spend hours checking sources, fixing grammar, and defending policies. They’re not experts in every topic—they’re just careful readers who care about getting it right. These volunteers follow Wikipedia policy, a set of community-agreed rules that govern how content is created and maintained, like neutral point of view, verifiability, and no original research. These aren’t suggestions—they’re the backbone of trust. If you’ve ever wondered why Wikipedia doesn’t just let anyone say anything, it’s because these policies stop chaos. They’re enforced by people, not bots, and they’re constantly debated. You can’t just add your opinion—even if you’re right. You need a reliable source to back it up.
That’s why Wikipedia neutrality, the rule that articles must fairly represent all significant viewpoints based on published sources matters so much. On topics like climate change, politics, or history, neutrality isn’t about being boring—it’s about being honest. It means giving space to minority views only if they’re well-documented, not because they’re popular. And it’s why Wikipedia bias, the uneven representation of topics due to gaps in who edits and what they focus on is such a big deal. Most editors are male, urban, and from wealthy countries. That skews coverage. But volunteer task forces are working to fix that—adding Indigenous knowledge, women’s history, and local stories that were left out. You won’t find this on the front page. You’ll find it in the quiet edits, the long discussions, the midnight copyediting drives. This is editing as a public service. And what you’ll see in the posts below is the full picture: how policy fights bias, how volunteers win small battles, how AI tries to interfere, and why, despite everything, Wikipedia still works.
How to Avoid Weasel Words and Vague Language on Wikipedia
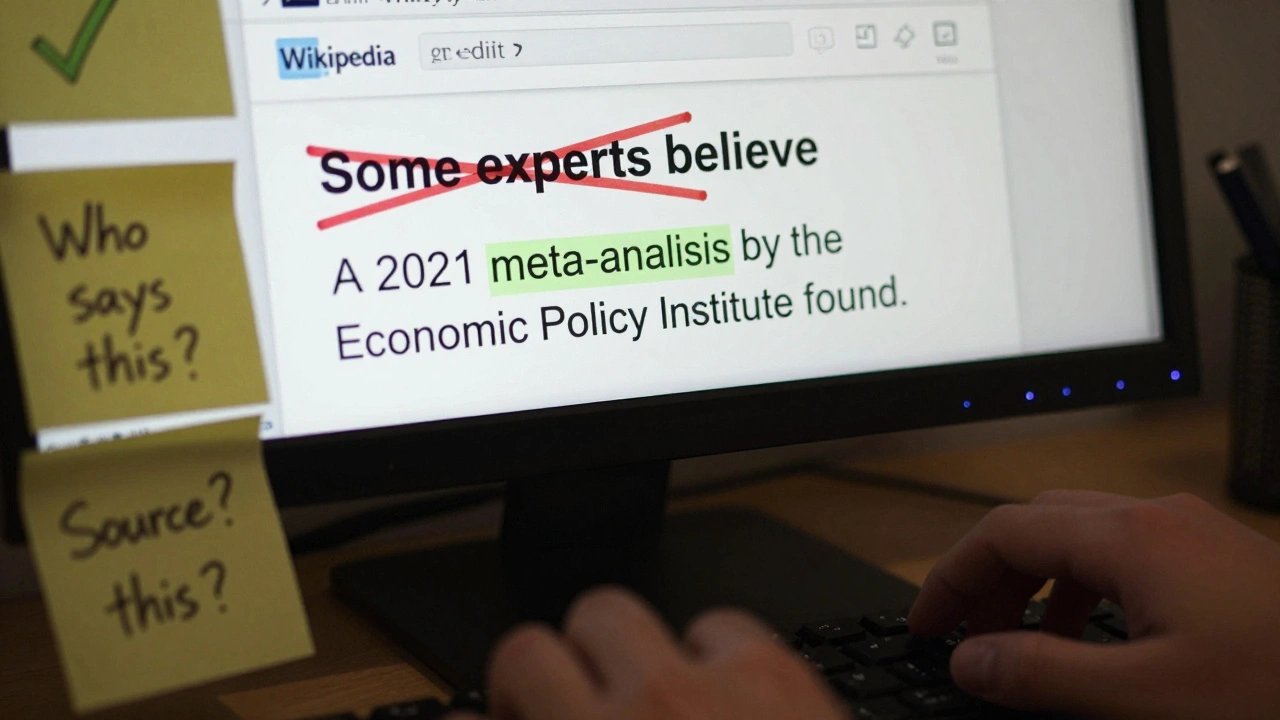
Learn how to spot and remove weasel words and vague language on Wikipedia to improve article accuracy, meet editorial standards, and build trust with readers using clear, sourced statements.
How to Write Neutral Lead Sections on Contentious Wikipedia Articles
Learn how to write neutral lead sections for contentious Wikipedia articles using verified facts, proportionality, and clear sourcing-without taking sides or using loaded language.
How to Spot POV Pushing and Original Research on Wikipedia
Learn how to spot biased edits and made-up claims on Wikipedia. Understand POV pushing and original research-two major threats to Wikipedia's neutrality-and what you can do to help keep it reliable.
Handling Living Person Disputes on Wikipedia: BLP Best Practices
Learn how to handle disputes over living person biographies on Wikipedia using the BLP policy. Discover what sources are valid, how to respond to false claims, and why neutrality matters more than speed.
Using Sandboxes to Plan Major Wikipedia Article Improvements
Learn how to use Wikipedia sandboxes to plan and test major article improvements before publishing. Avoid reverts, build consensus, and create higher-quality content with proven editing practices.
How to Request a Copyedit at the Wikipedia Guild of Copy Editors
Learn how to request a copyedit from the Wikipedia Guild of Copy Editors to improve article clarity, grammar, and readability. Step-by-step guide for editors aiming for higher quality standards.
Wikipedia Editing Challenges and Backlog Drives This Month
Wikipedia's editing backlog has hit record levels, with over 300,000 unreviewed edits. Volunteer editors are overwhelmed as new contributors face steep barriers and outdated tools. Here's why the system is straining-and how you can help.
How to Detect and Remove Original Research on Wikipedia
Learn how to identify and remove original research on Wikipedia - the key policy that keeps the encyclopedia reliable. Understand what counts as unsourced analysis and how to fix it without breaking community rules.
Redirect and Move Tools on Wikipedia: Avoiding Common Mistakes
Learn how to use Wikipedia's redirect and move tools correctly to avoid breaking links, confusing readers, and triggering community backlash. Essential for any editor who wants to maintain the encyclopedia's integrity.
New WikiProject Launches and Focus Areas on Wikipedia
Six new WikiProjects launched on Wikipedia in 2025 to fix gaps in coverage of Indigenous languages, disability history, rural healthcare, climate migration, women in STEM, and local histories. These community-driven efforts are transforming who gets represented on the world’s largest encyclopedia.
How Wikipedia Updates Articles After Major News Events
Wikipedia updates articles after major news events by relying on verified sources and a global network of volunteer editors. It prioritizes accuracy over speed, waiting for confirmation before making changes. This process keeps it more reliable than many news outlets in the first hours after breaking news.
How to Handle Rumors and Unconfirmed Reports on Wikipedia
Learn how Wikipedia handles rumors and unconfirmed reports, why they're removed quickly, and how you can help prevent false information from spreading on the world's largest encyclopedia.