Wikipedia responses to criticism: How the platform handles backlash, bias, and change
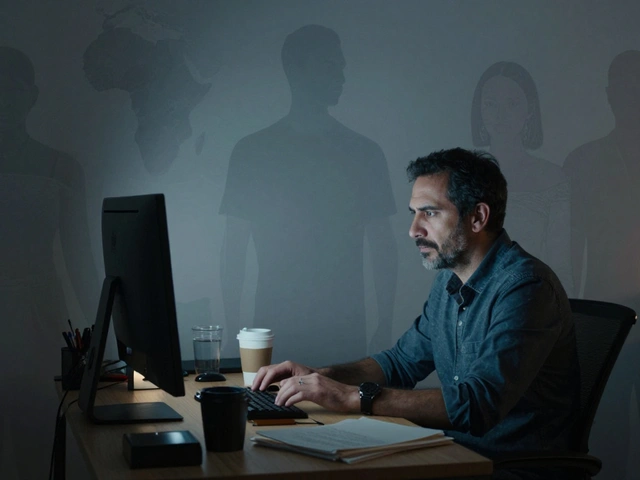
When people say Wikipedia is biased, incomplete, or unreliable, it doesn’t just ignore them—it Wikipedia responses to criticism, the collective ways editors, policies, and tools react to public and internal challenges to its credibility. Also known as Wikipedia accountability mechanisms, it’s not about defending the site—it’s about fixing it, one edit at a time. This isn’t a top-down system where executives issue corrections. It’s a living network of volunteers who track criticism, analyze patterns, and adjust rules to stay credible. When a study points out that women’s biographies are underrepresented, editors don’t wait for permission—they start edit-a-thons. When journalists call out inaccuracies in breaking news coverage, Wikipedia’s edit filters, automated systems that detect vandalism and policy violations on high-risk articles get updated. And when academics argue their research is misrepresented, the community responds with clearer guidelines on conflicts of interest, rules that prevent self-promotion while still allowing experts to improve articles ethically.
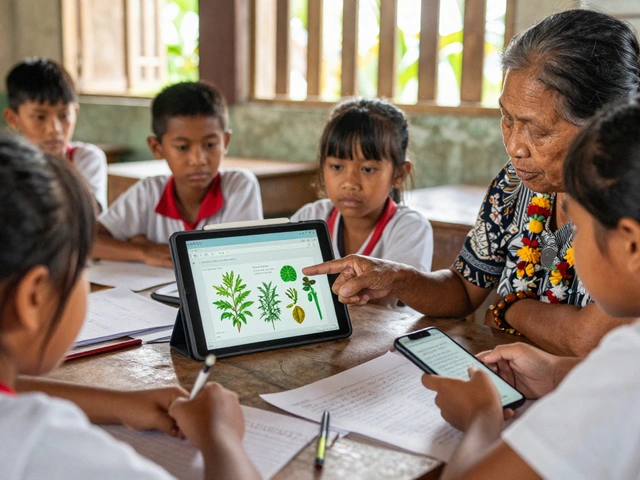
Wikipedia doesn’t claim to be perfect. It admits its gaps—like how it excludes oral traditions, knowledge passed down verbally in cultures without written records because its rules demand published sources. That’s not neutrality. It’s a flaw. And the community knows it. Groups like GLAM-Wiki are working with museums and Indigenous communities to bring those stories in, using legal archives and partnerships. Meanwhile, Wikidata, a central database that shares facts across 300+ Wikipedia languages helps reduce translation errors and keeps facts consistent, even when local editors disagree. When criticism comes from newsrooms, Wikipedia doesn’t shut them out—it invites them in. Journalist roundtables help reporters understand how to use Wikipedia responsibly, while the Signpost, a community-run news outlet that tracks Wikipedia’s internal debates and changes reports on every major policy shift, backlash, or reform—publicly and transparently.
What you’ll find in this collection isn’t a defense of Wikipedia. It’s a window into how it learns. From how Wikipedia responses to criticism shape its copyright rules to how edit histories let anyone trace the fix to a biased sentence, these stories show a system built to adapt. You’ll see how mentorship keeps editors from burning out, how film release weeks reveal public interest in real time, and why a simple tool like Huggle can stop a wave of vandalism before it spreads. This isn’t about winning arguments. It’s about building something that lasts—even when the world keeps pointing out its cracks.
Media Criticism of Wikipedia: Common Patterns and How Wikipedia Responds
Media often criticizes Wikipedia for bias and inaccuracies, but its open model allows rapid correction. This article explores common criticisms, how Wikipedia responds, and why it remains the most transparent reference tool online.